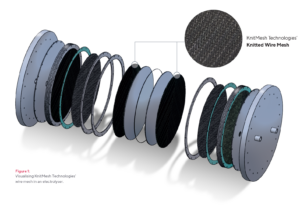
KnitMesh Technologies’ Gas Diffusion Layers are specialised components made of knitted wire mesh. These layers are commonly employed in electrolysis processes for hydrogen production and chlor-alkali applications.
Download BrochureScroll Down
KnitMesh Technologies’ Gas Diffusion Layers are an essential component in various applications such as proton exchange membranes (PEM), ion exchange membranes (IEM), and alkaline zero-gap electrolyser setups. These specialised layers play a crucial role in improving efficiency and optimising performance in electrochemical processes.
Constructed from high-quality knitted wire mesh, KnitMesh Technologies’ Gas Diffusion Layers are designed to facilitate the smooth passage of liquids, gases, or particles while providing robust structural support. The unique crimped or compressed design of these layers ensures that they meet specific requirements for each application, ensuring maximum effectiveness.
One of the key benefits of KnitMesh Technologies’ Gas Diffusion Layers is their ability to eliminate electrical contact resistance by enhancing electrical and pressure contact between different components within electrolysis cell stacks and modular cell cartridges. By optimising the connectivity between cells, divider stacker plates, membranes, and diaphragms, these layers help improve overall efficiency and performance.
To further enhance electrical conductivity, KnitMesh Technologies offers the option to weld Gas Diffusion Layers to various contact points on metal plates and adjacent components such as bipolar plates, porous structures, metallic felt, and expanded metal. This seamless integration ensures a single, bonded structure that effectively reduces electrical contact resistance, resulting in superior performance.

In 2025, KnitMesh Technologies partnered with a leading manufacturer of woven wire mesh, giving you access to an even broader range of solutions. You can now source both knitted wire mesh and woven wire mesh directly from a single, trusted supplier. These materials can be combined, including welded together, to create a complete and fully integrated solution tailored to your needs. In addition, KnitMesh Technologies can now also supply full electrolyser cell assemblies, helping you streamline your supply chain and simplify your hydrogen projects.
Electrolysis is the process of breaking down a substance into its individual components using an electric current. This process is widely used in industry as well as in scientific research. In simple terms, electrolysis involves the use of an electrolytic cell that consists of two electrodes, an anode and a cathode, and an electrolyte solution that conducts electricity.
When an electric potential is applied across the anode and cathode, the ions in the electrolyte solution move towards their respective electrodes due to the attraction of opposite charges. At the anode, positive ions lose their electrons and become oxidised, while at the cathode, negative ions gain electrons and become reduced. This results in the formation of new substances, which can be isolated through various processes.
One important application of electrolysis is in the production of hydrogen gas, which is used in various industries as well as for energy production. In this process, water is used as the electrolyte solution, and the electric current is used to split the water molecule into its constituent hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
An essential component in an electrolyser system is the Gas Diffusion Layer. Gas Diffusion Layers are porous, conductive sheets that are placed on the surface of the electrodes to facilitate the transport of reactant gases to and from the electrode surface. They also help to evenly distribute the reactant gases, provide electrical conductivity, and manage water within the cell.